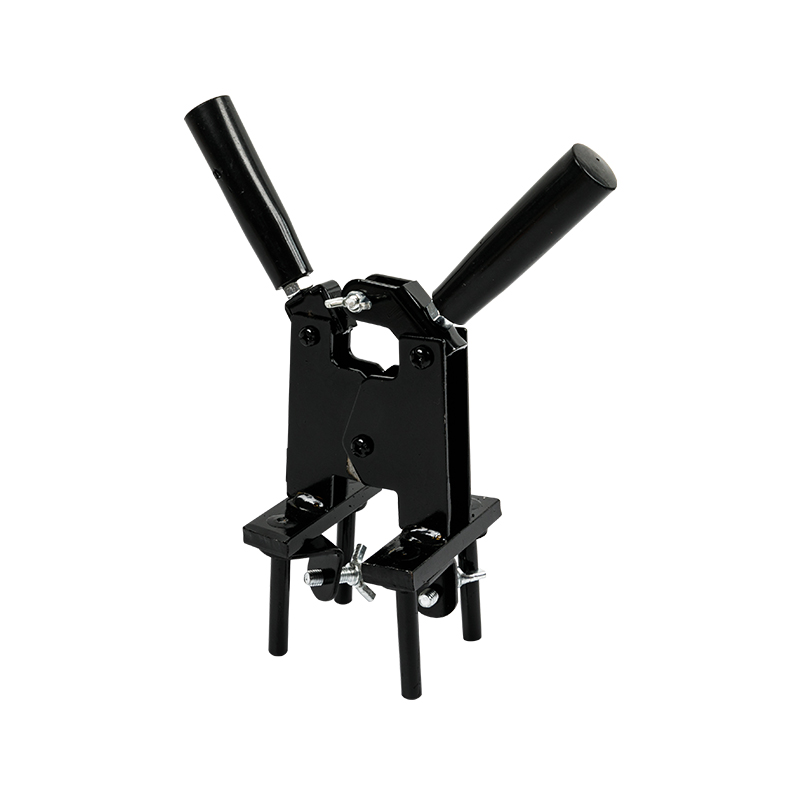
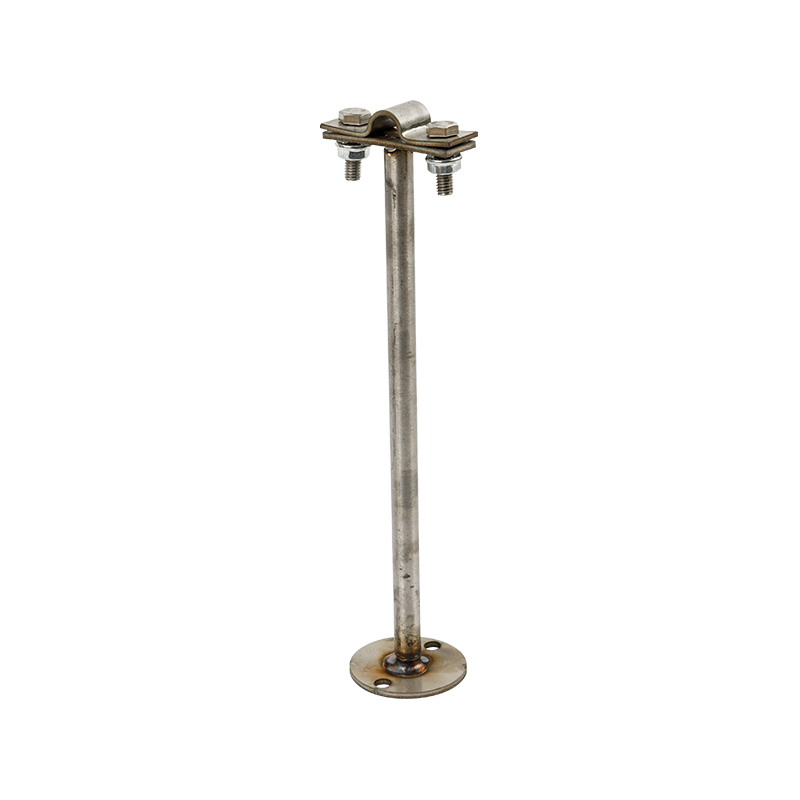
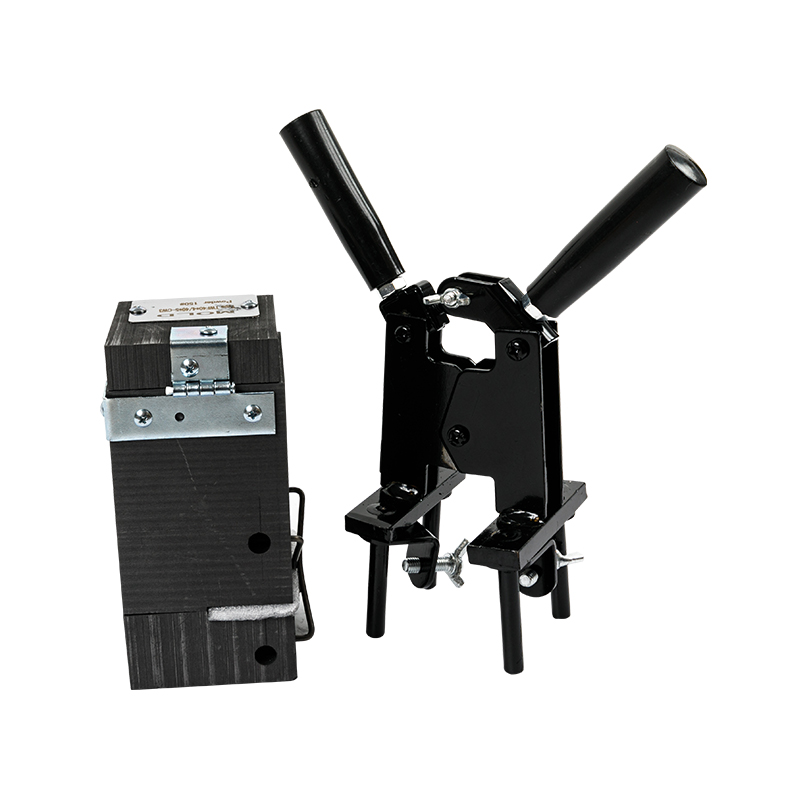
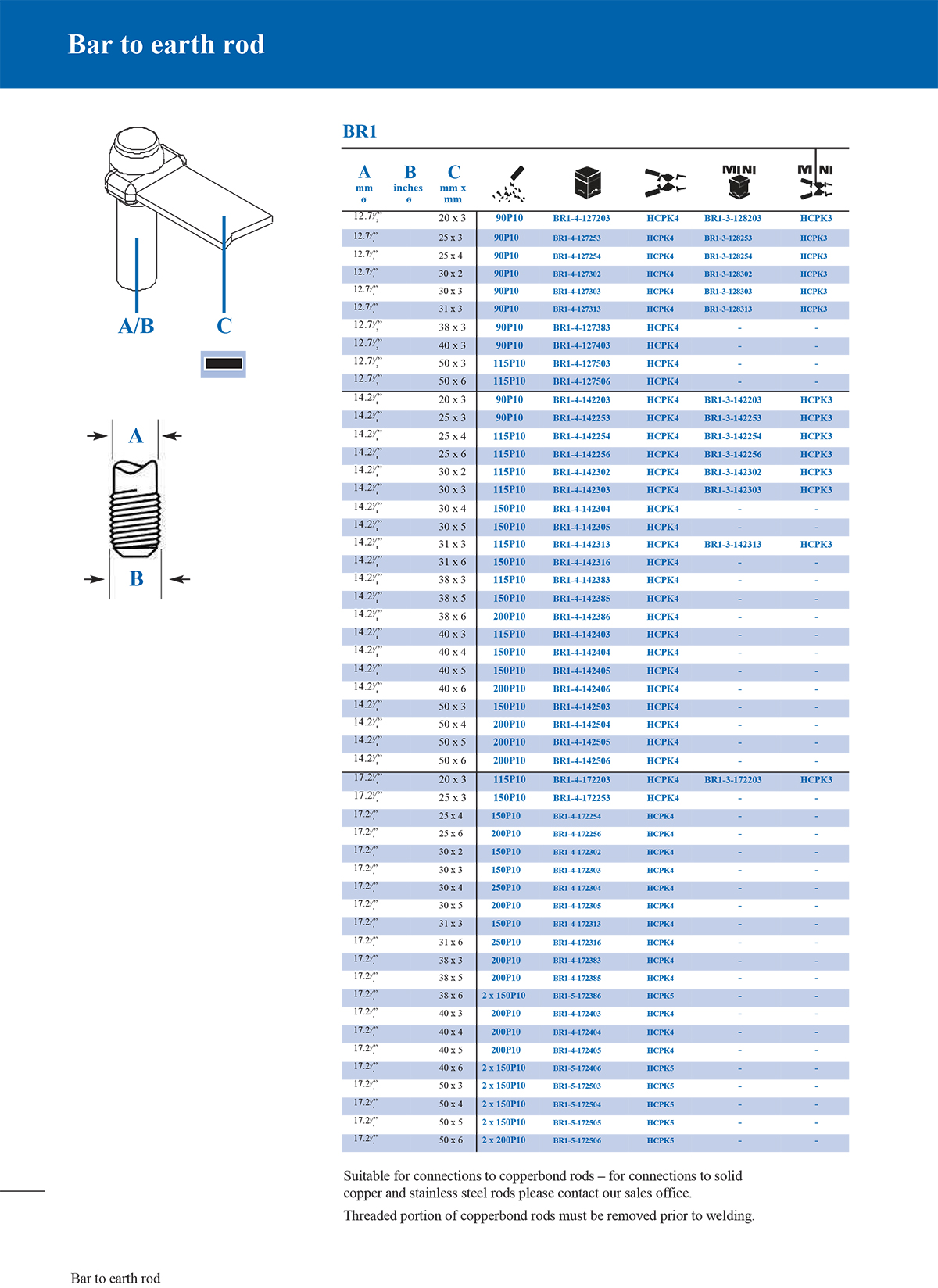
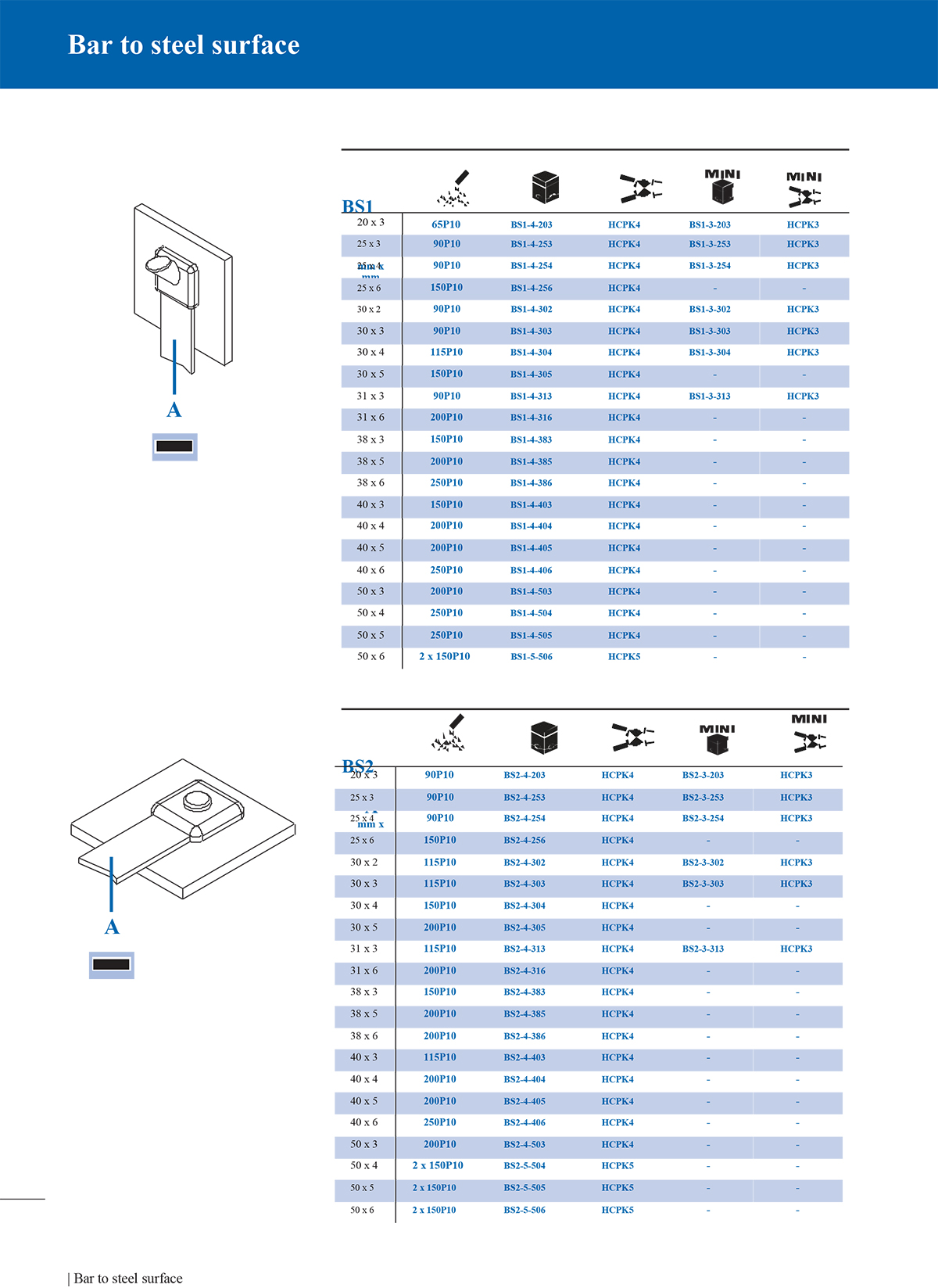
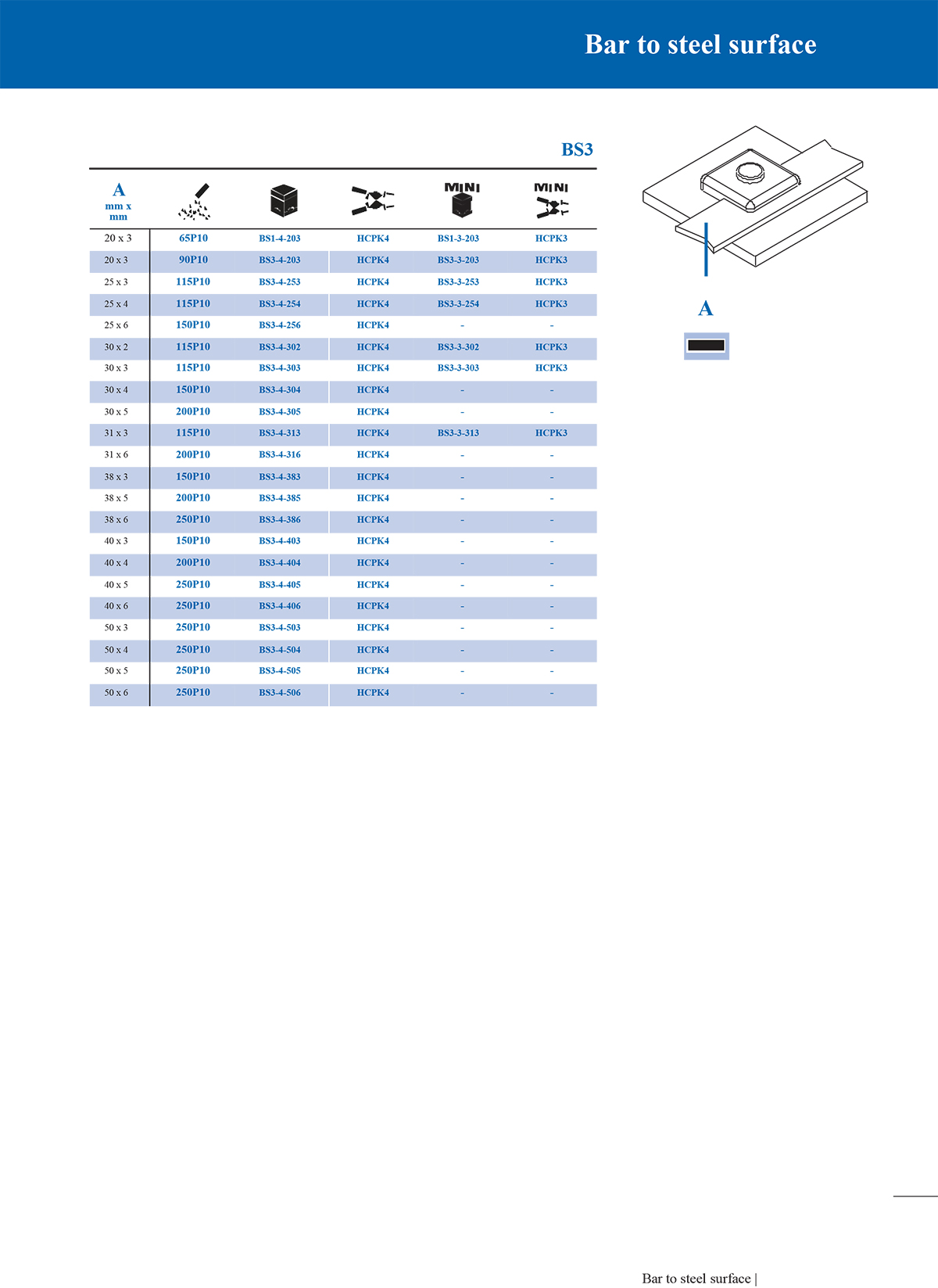
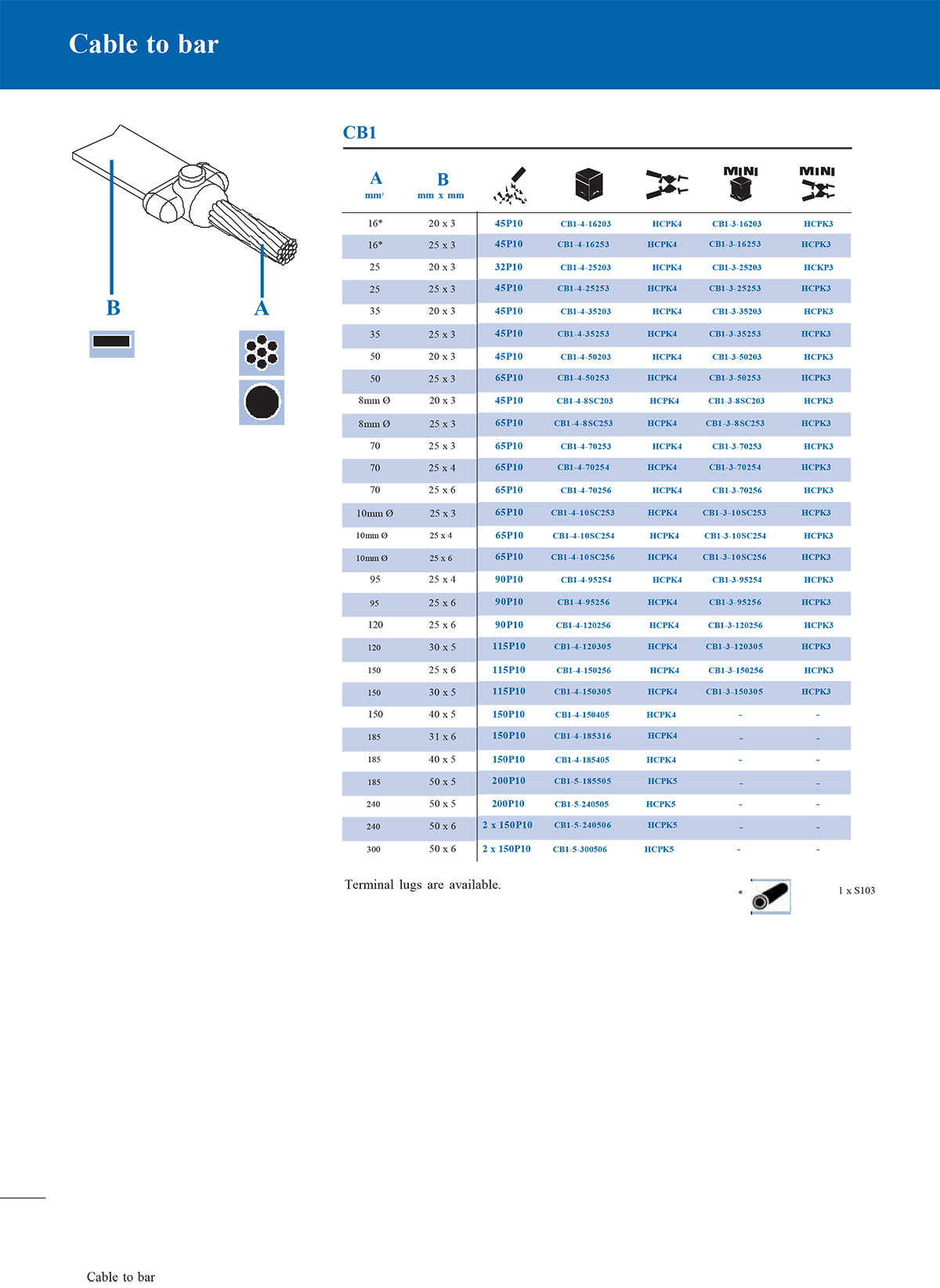
Exothermic soldering is a simple, high-efficiency, high-quality metal joining process that utilizes the chemical reaction heat of a metal compound as a heat source, through superheated (reduced) molten metal, directly or indirectly heated, in a special graphite mold A welded joint with a certain shape and size in accordance with engineering requirements is formed in the welding chamber. At present, exothermic welding has generally replaced the mechanical and physical connection methods between metals in the past. Many international standards recommend the use of exothermic welding processes in grounding systems, such as IEEE, IEC, NEC, ASME, etc.
-
Exothermic welding reaction principle
3Cu2O+2AL—6Cu+Al2O3+Heat(2537℃)
Advantages of Exothermic welding
The generated solder joint is pure copper, which is a permanent atomic bond. The corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity and mechanical strength of the solder joint are not lower than the conductor itself, and the problem that the mechanical and physical connection is easy to loosen is avoided;
The reinforced integrated heat-dissipating flux is non-dangerous. It adopts sealed waterproof design. The flux does not contain harmful materials such as phosphorus and magnesium, which is convenient for transportation and storage.
The precise component packaging can be provided according to the connection mode, and under the premise of fully ensuring the standardization of the welding quality, the damage of the metal base material by welding is not only minimized, but also the service life of the mold is greatly improved;
The welding method is simple and easy, no professional skill is required, the quality of the welding point is high, the materials and tools for welding are light in weight, easy to carry, no external power source or heat source is needed for welding; high-strength, high-purity high-quality graphite raw materials are used to produce the mold. The graphite has high compactness to ensure the lowest adhesion of the welding residue and the longest service life of the mold. From the reaction, diversion to welding design is reasonable, to avoid mold explosion, welding copper splash and other phenomena, welding quality is high;
-
-

about us
Our Story
Xinchang TuAn Machinery Co., Ltd.Rooted in the past, facing the future?
Based on customer needs, connect the products and technologies required by customers with the scientific research capabilities of universities to achieve innovation based on customer needs.
TuAn is famous China Exothermic Welding Mould manufacturers and Exothermic Welding Mould factory, the company continuously strengthens cooperation with upstream and downstream enterprises, rapidly expands comprehensive service capabilities, and transforms from a single lightning protection enterprise to a comprehensive large-scale project supporting enterprise. After years of accumulation, TuAn has formed a stable customer base covering important fields such as petroleum and petrochemical, high-speed rail, and electric power.
Recommended Products
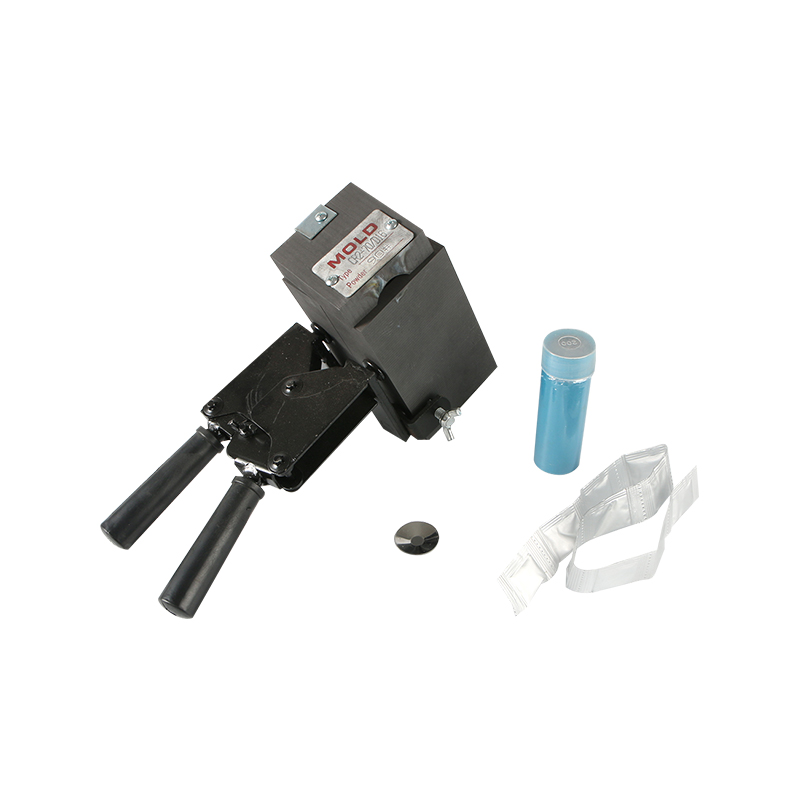
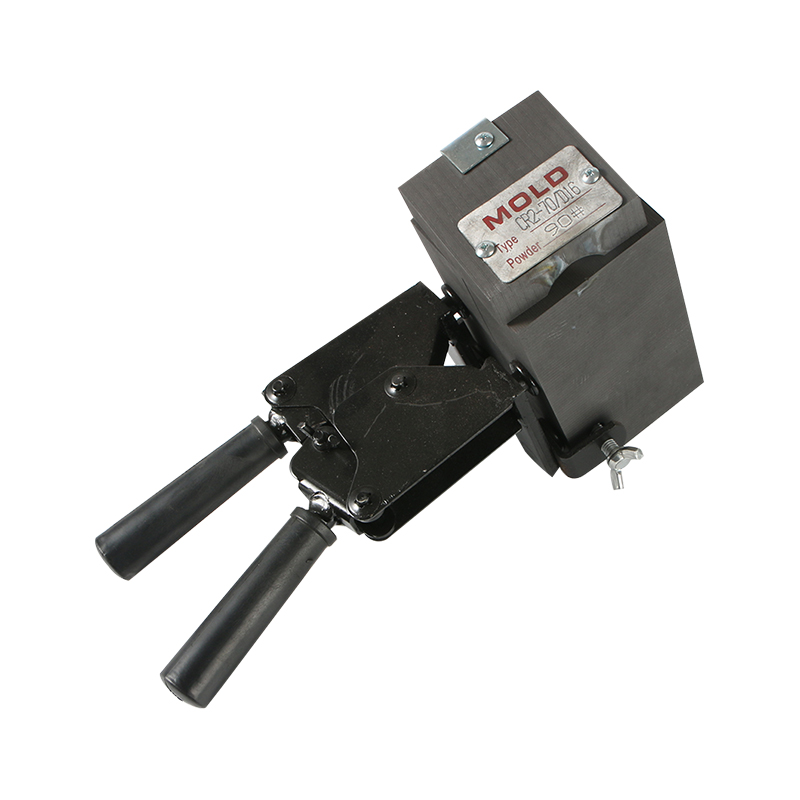
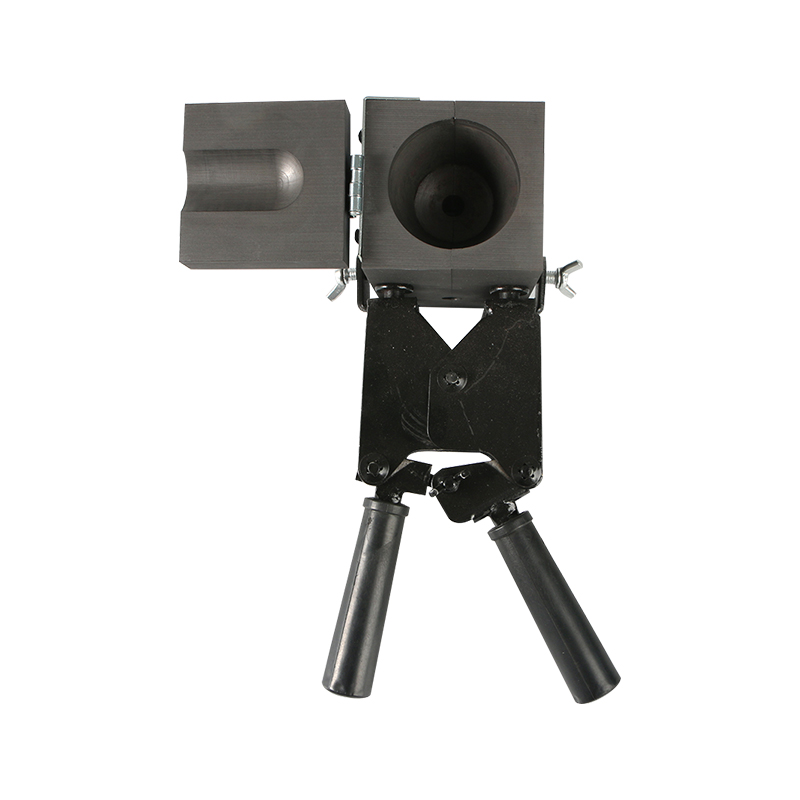
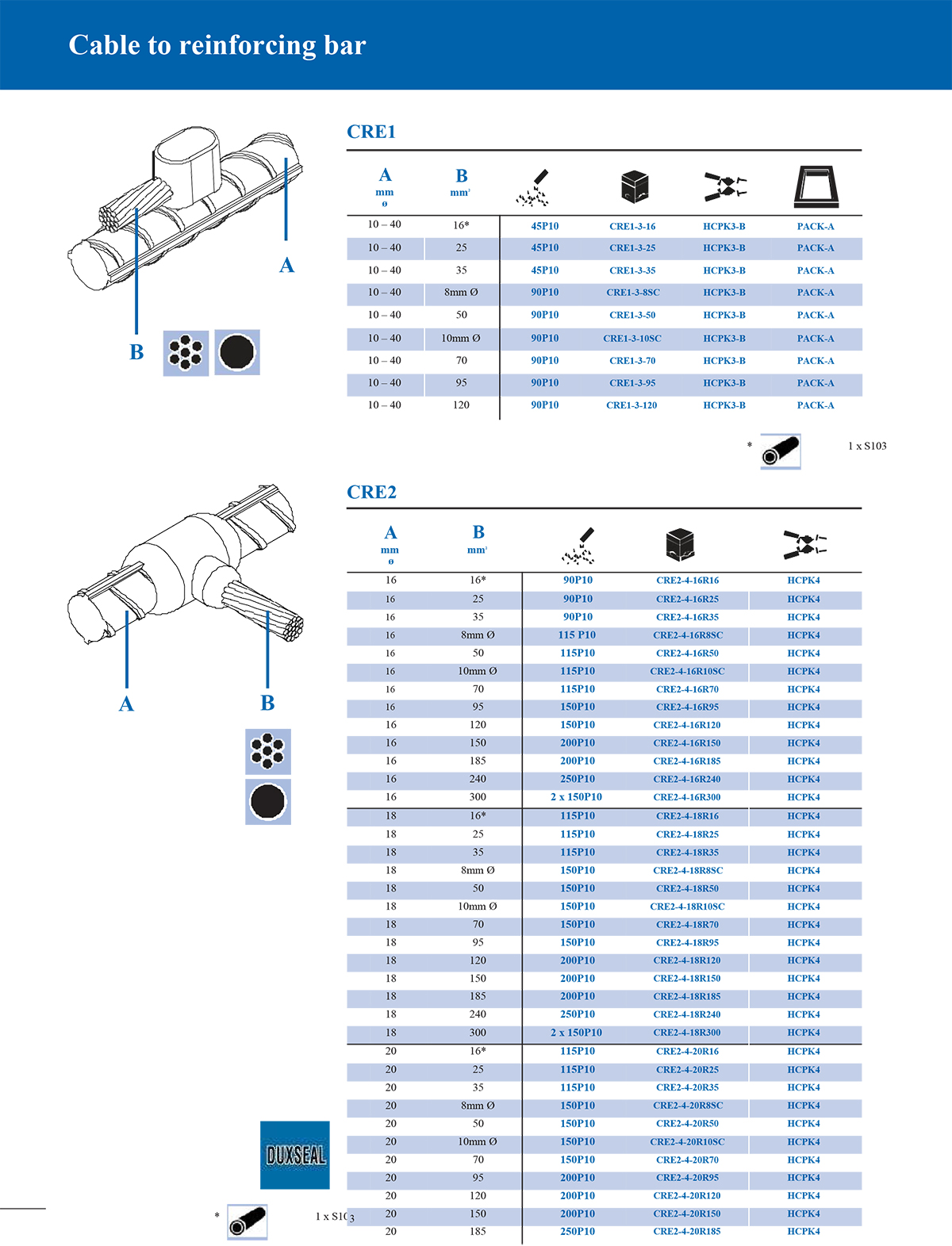
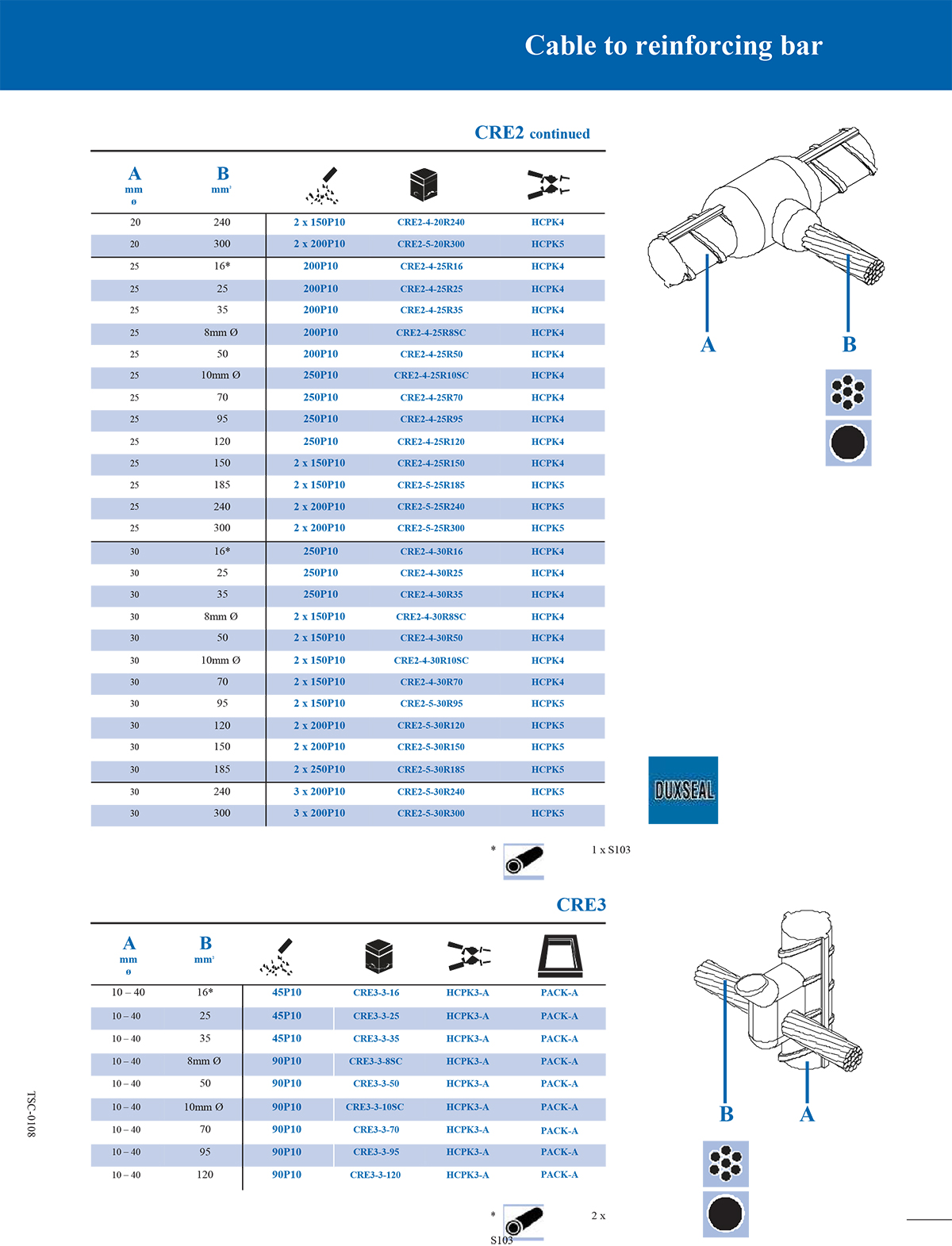
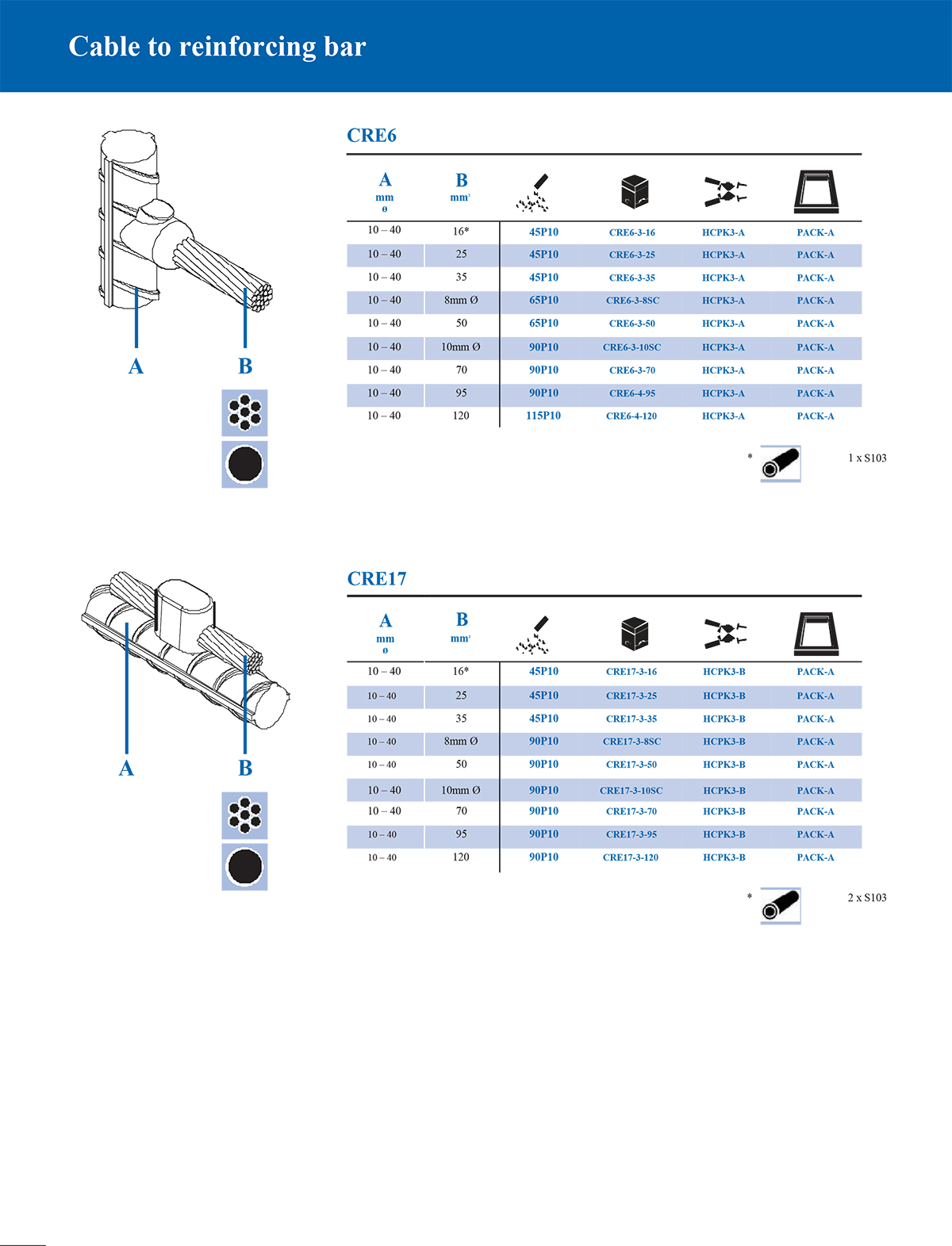
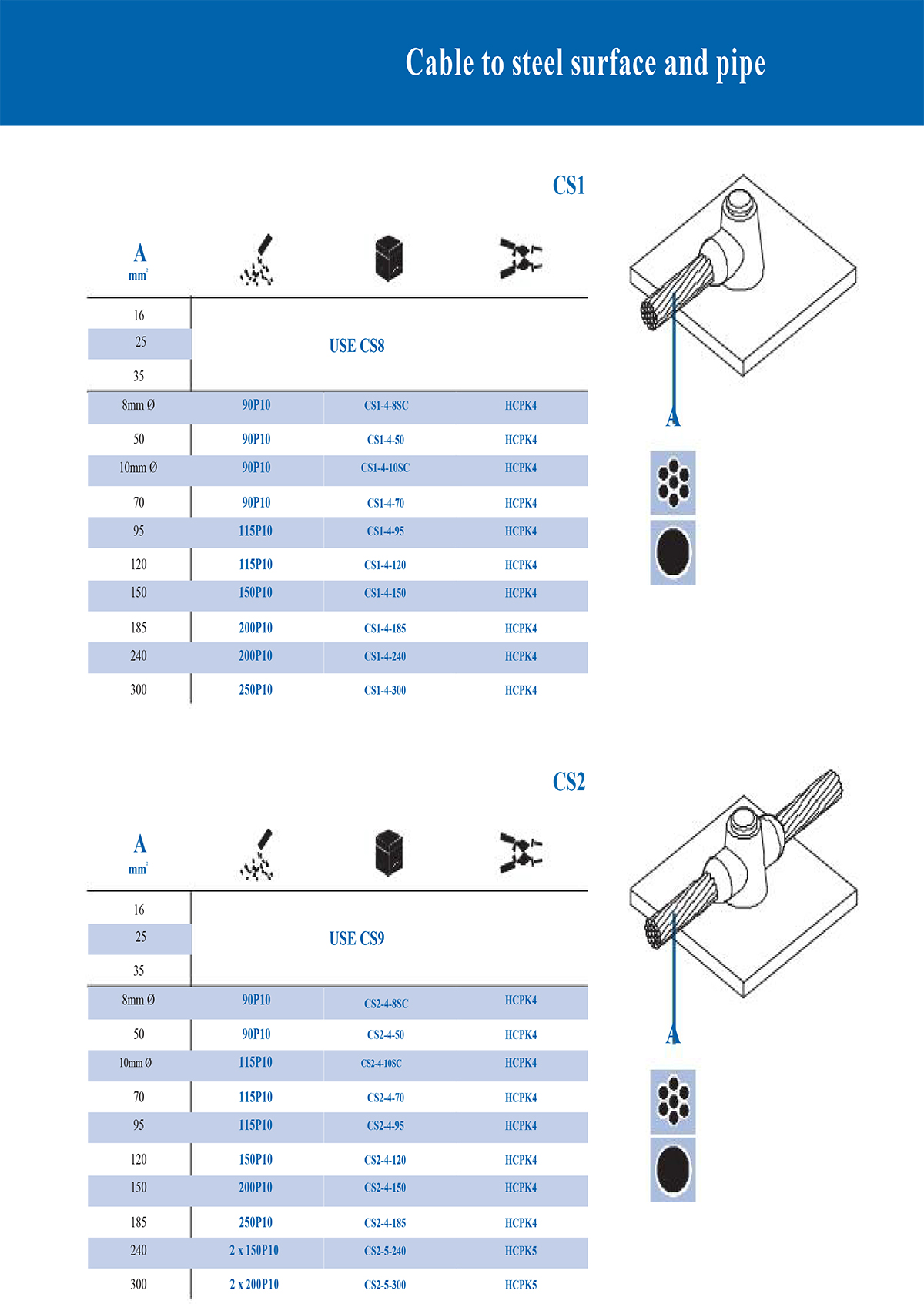
What is an exothermic welding mould and what are the common types?
Basic definition of exothermic welding mould
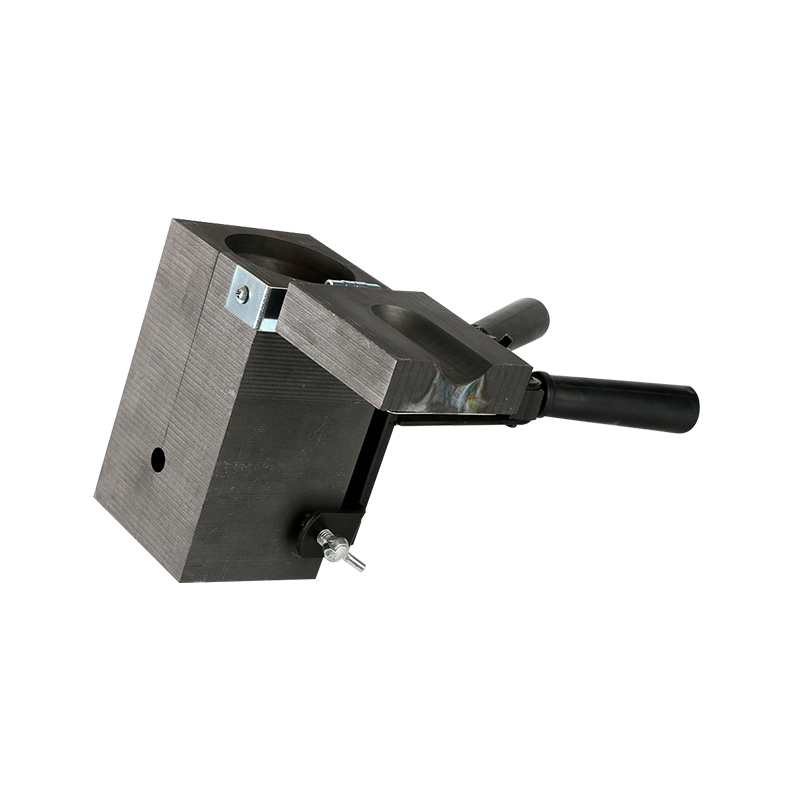
Exothermic welding mould is a high-temperature heat-resistant mould used to realize exothermic welding process, usually made of high-purity graphite material. Exothermic welding is a method of melting metal by generating high temperature through aluminothermic reaction, thereby achieving permanent electrical connection between two conductors. The mould is a key component in this process, and its shape and structure directly determine the quality and form of the welded joint.
Exothermic welding mould not only has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high thermal conductivity, and easy processing, but also can effectively control the flow direction and cooling rate of molten metal. Through the cavity design inside the mould, a variety of connection forms can be formed, which is suitable for grounding systems, cable connections, lightning protection network connections and other projects in different occasions.
Main materials and structural characteristics of the mould
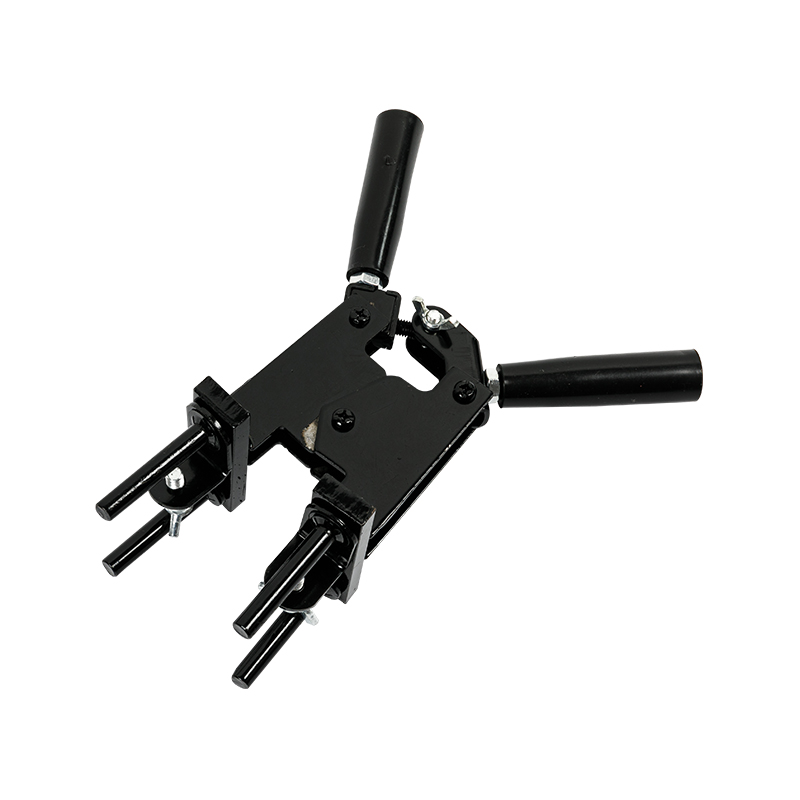
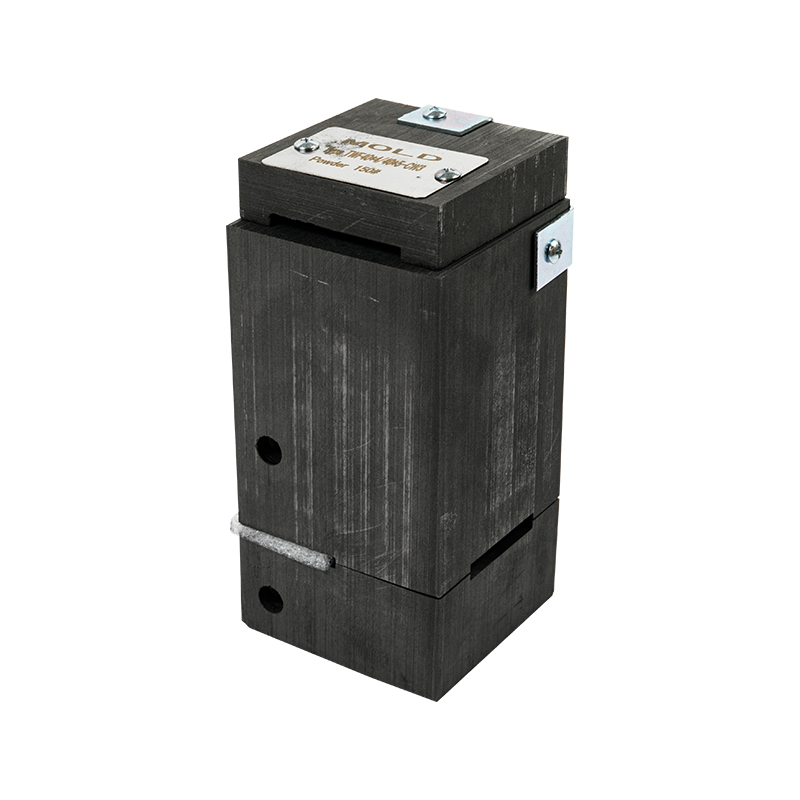
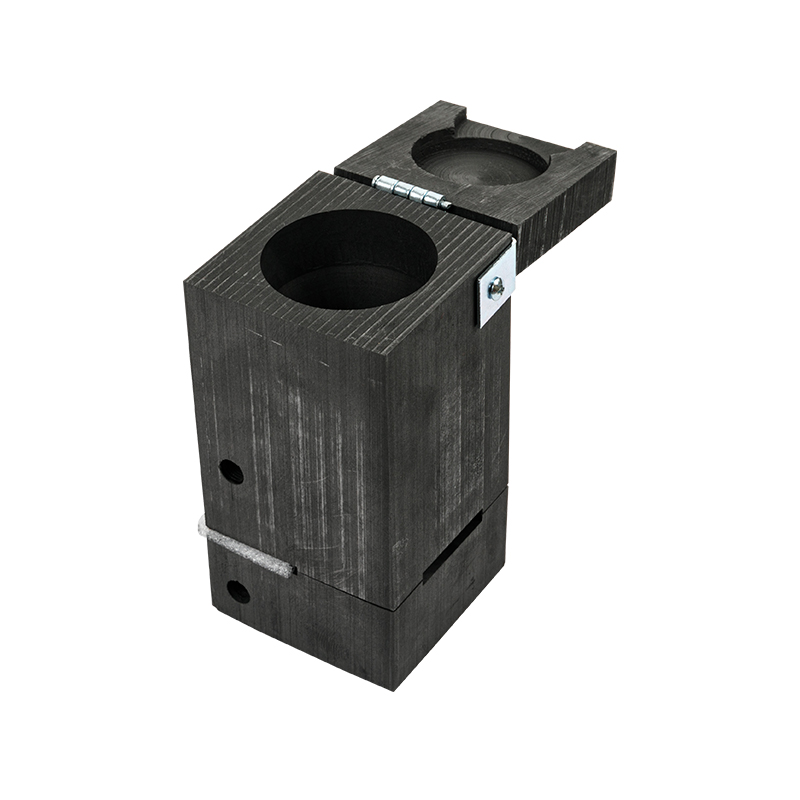
Common exothermic welding moulds mainly use isostatic graphite, which has good heat resistance and thermal shock resistance, and can withstand the high temperature released instantly by aluminothermic reaction. Its mould structure usually consists of two parts: the upper mould and the lower mould. The joint is a butt-jointed structure, and is equipped with functional areas such as positioning holes, guide grooves, and exothermic powder cavities.
The surface treatment of the mould mainly maintains the natural graphite state, and some high-end products may be coated with an anti-oxidation layer to extend the service life. The structural design needs to consider factors such as the deformation, flow path and cooling shrinkage of the welding material to ensure the consistency of the welding quality.
The role and scope of application of exothermic welding moulds
Exothermic welding moulds are widely used in power grounding systems, lightning protection grounding networks, rail transit, building lightning protection, petrochemicals, and signal systems. In these fields, it is necessary to achieve a stable electrical connection between metal conductors, and the connection is usually required to have the characteristics of corrosion resistance, low resistance, and high mechanical strength.
The connector formed by the exothermic welding mould is a molecular-level fusion state, which does not require additional power or pressure sources and can operate in an outdoor power-free environment. This connection method is suitable for connections between various metal materials, such as copper and copper, copper and steel, steel and steel, etc.
Common classification of exothermic welding mould types
According to different welding structures and connection requirements, exothermic welding moulds can be divided into many types. The following are several common types:
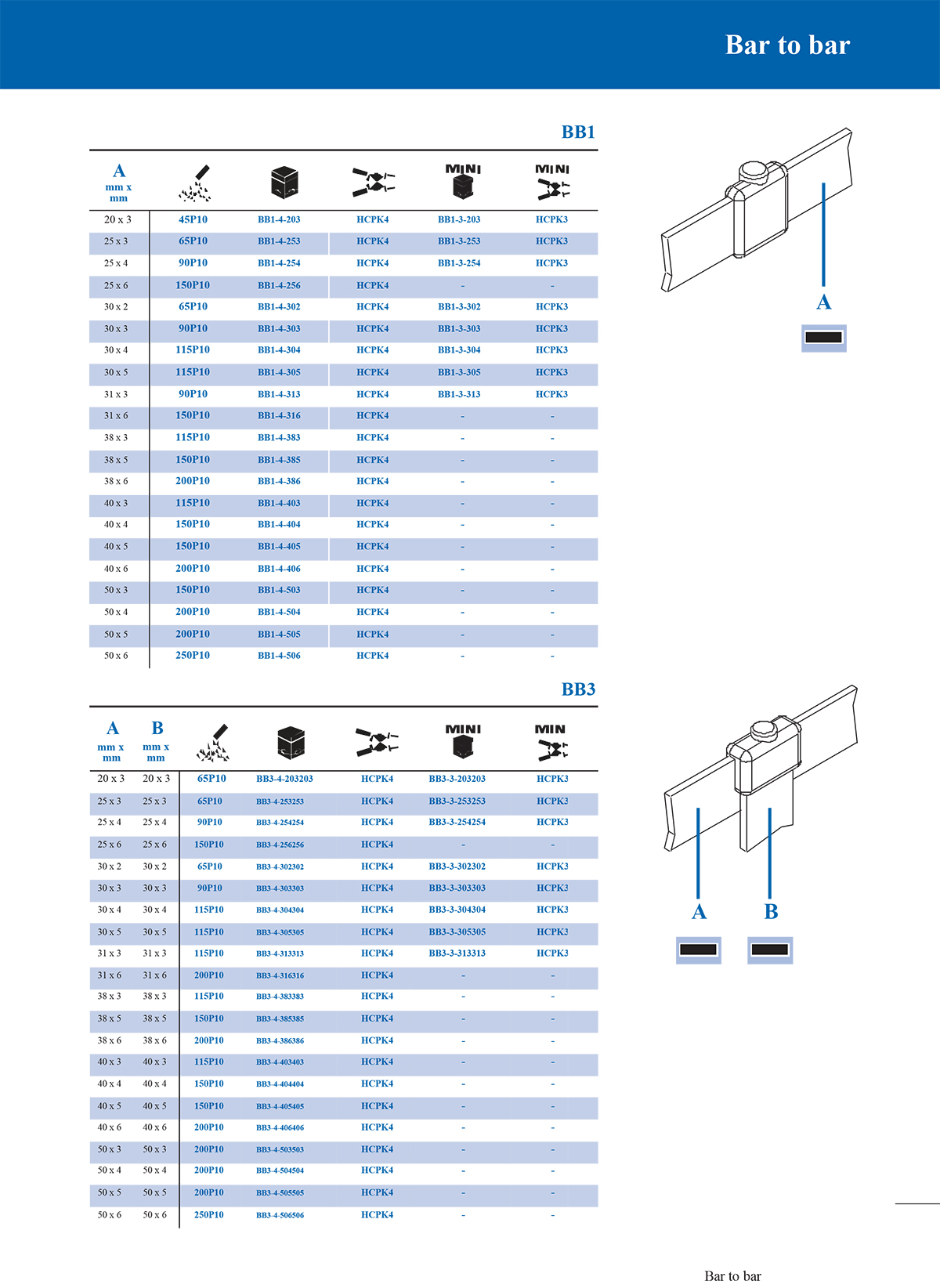
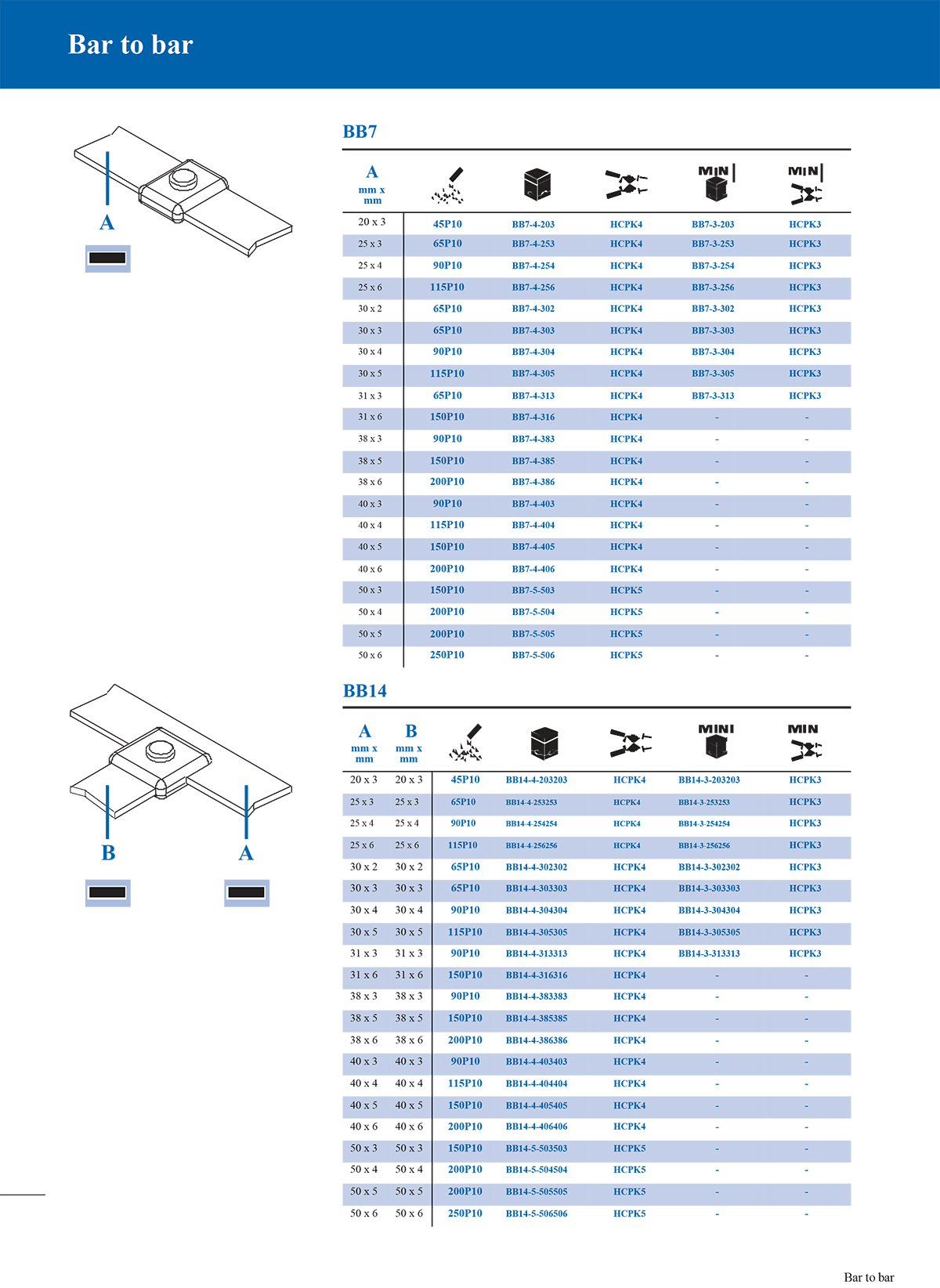
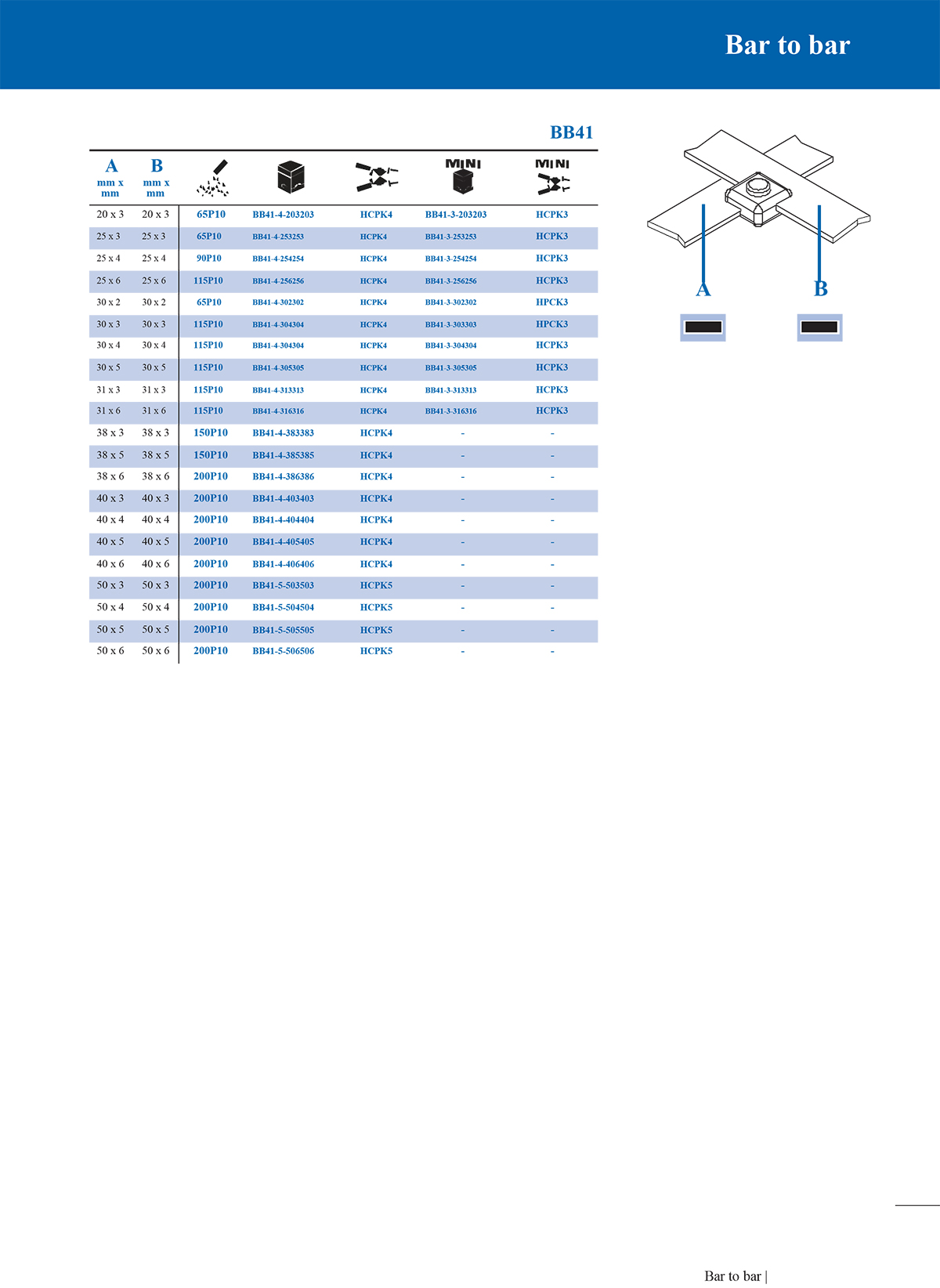
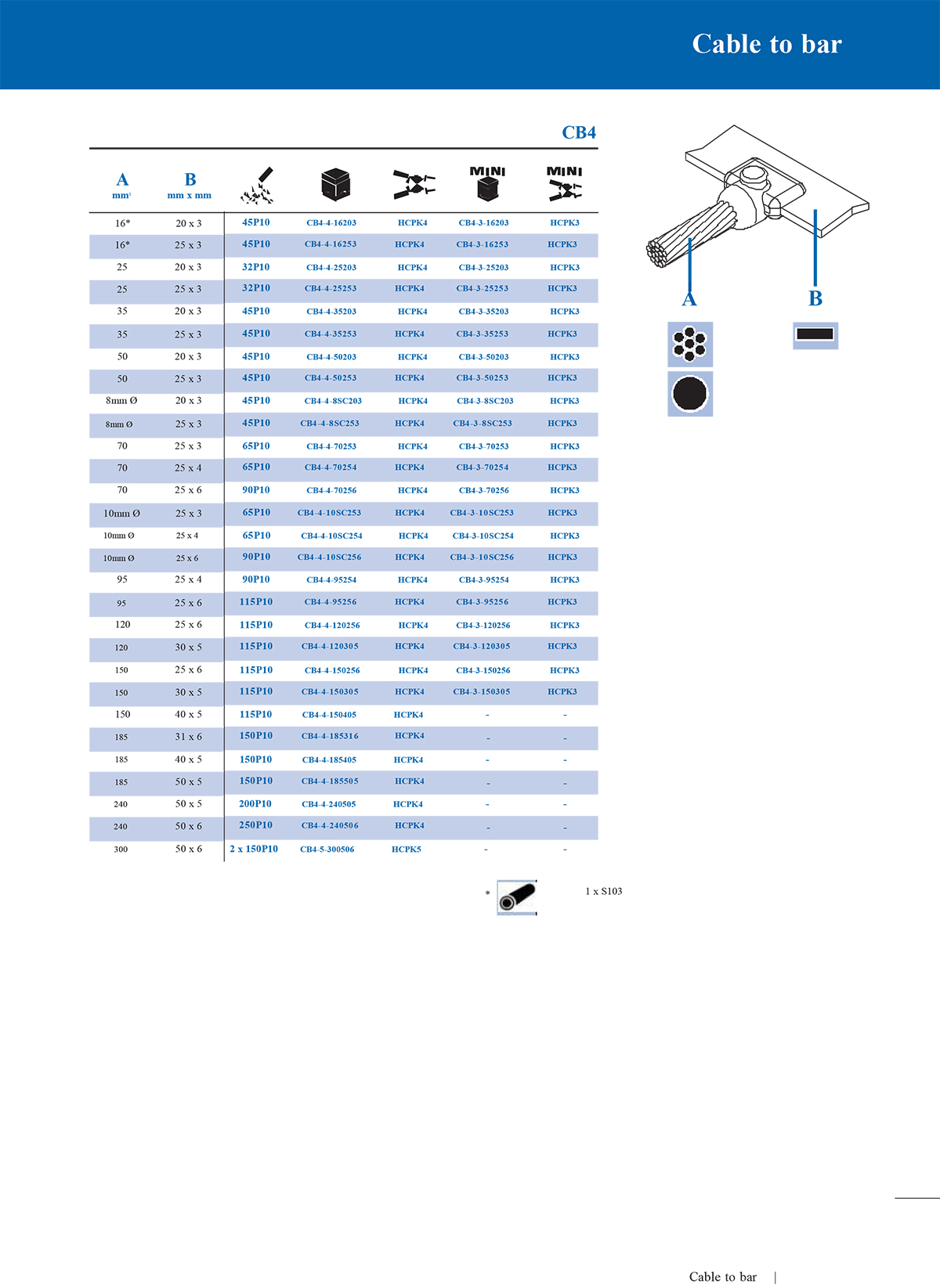
1. T-type connection mould
T-type moulds are used to connect a horizontal main conductor and a vertical branch conductor. The shape is like a "T" and is often used in cable branches, grounding trunks and branch lines.
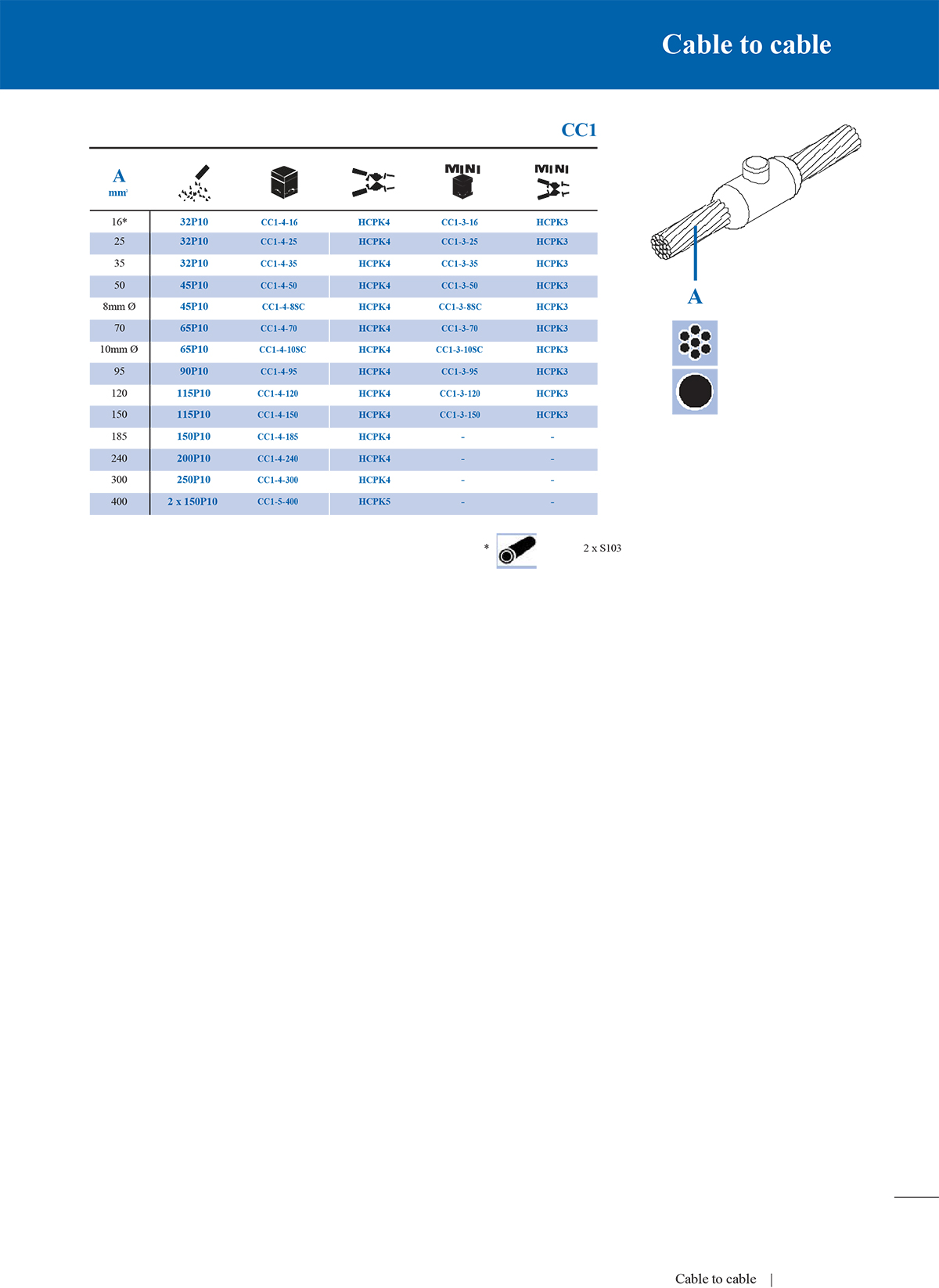
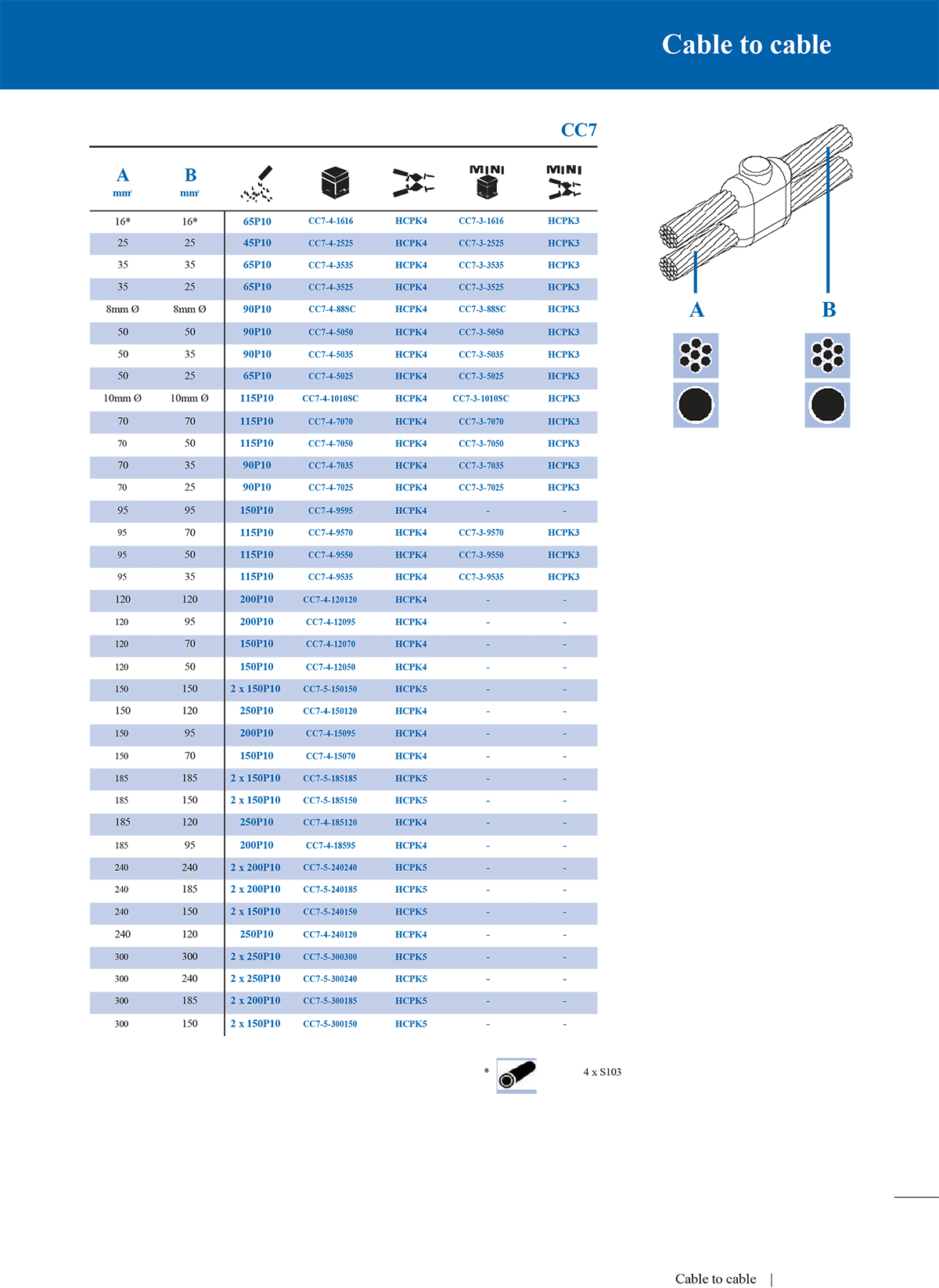
2. Straight connection mould
Straight moulds are suitable for axial butt connection of two conductors. The welding joint is in a straight line, which is suitable for extending the wire or restoring the integrity of interrupted cables.
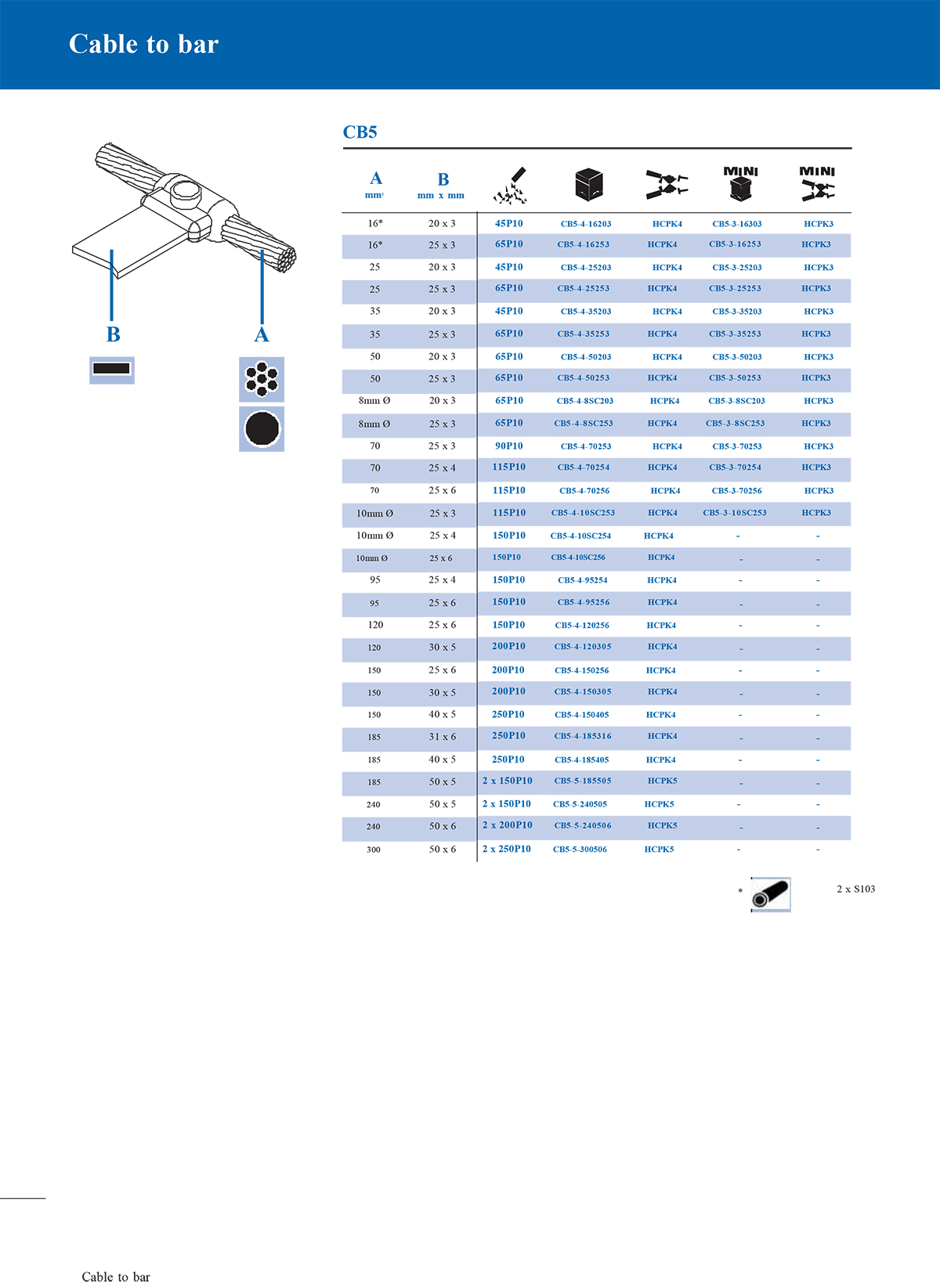
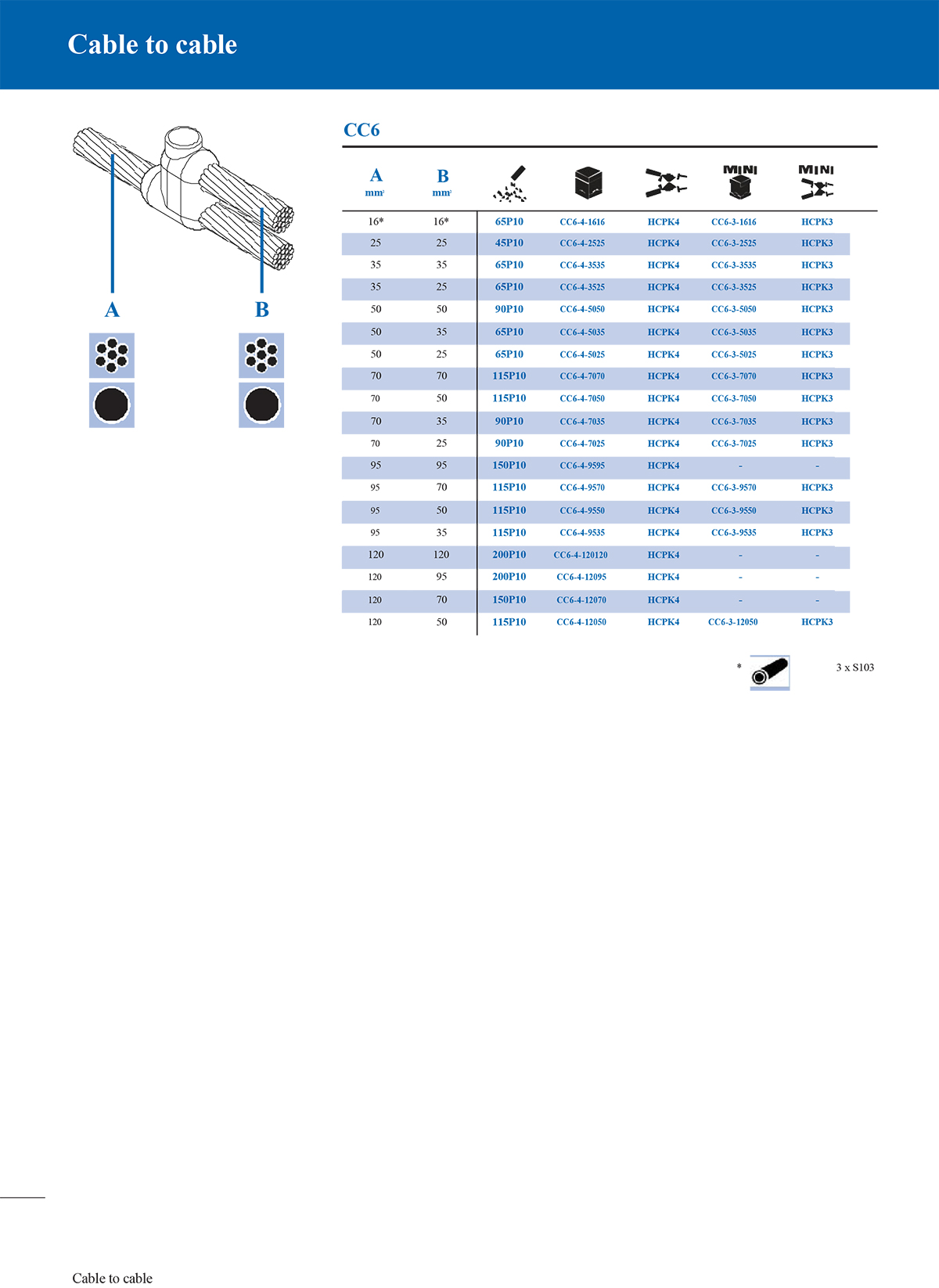
3. Overlap connection mould
This mould is used to connect two conductors in a partially overlapping manner. It is common in the parallel overlap of copper bars and steel bars to enhance electrical and mechanical connections.
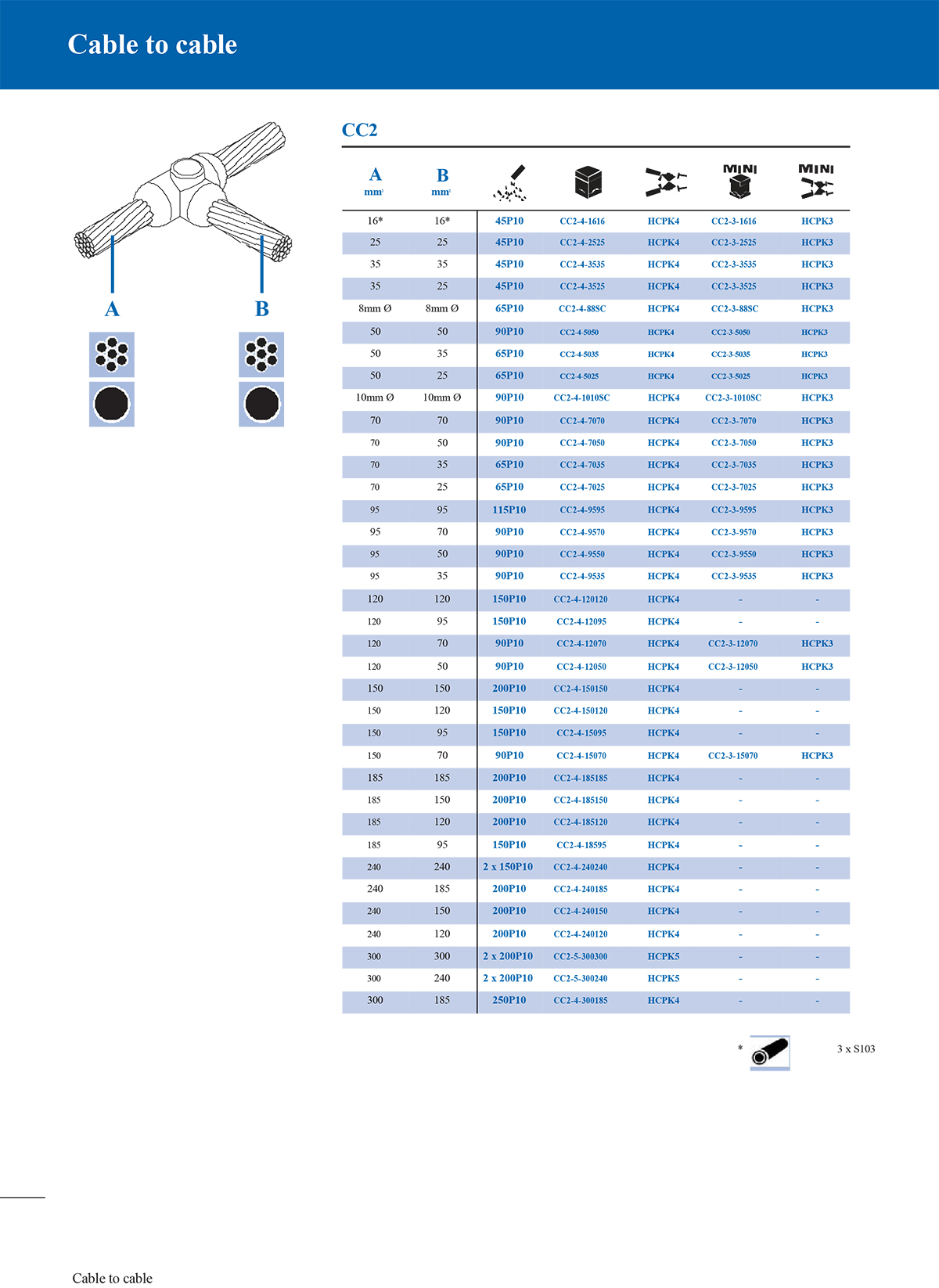
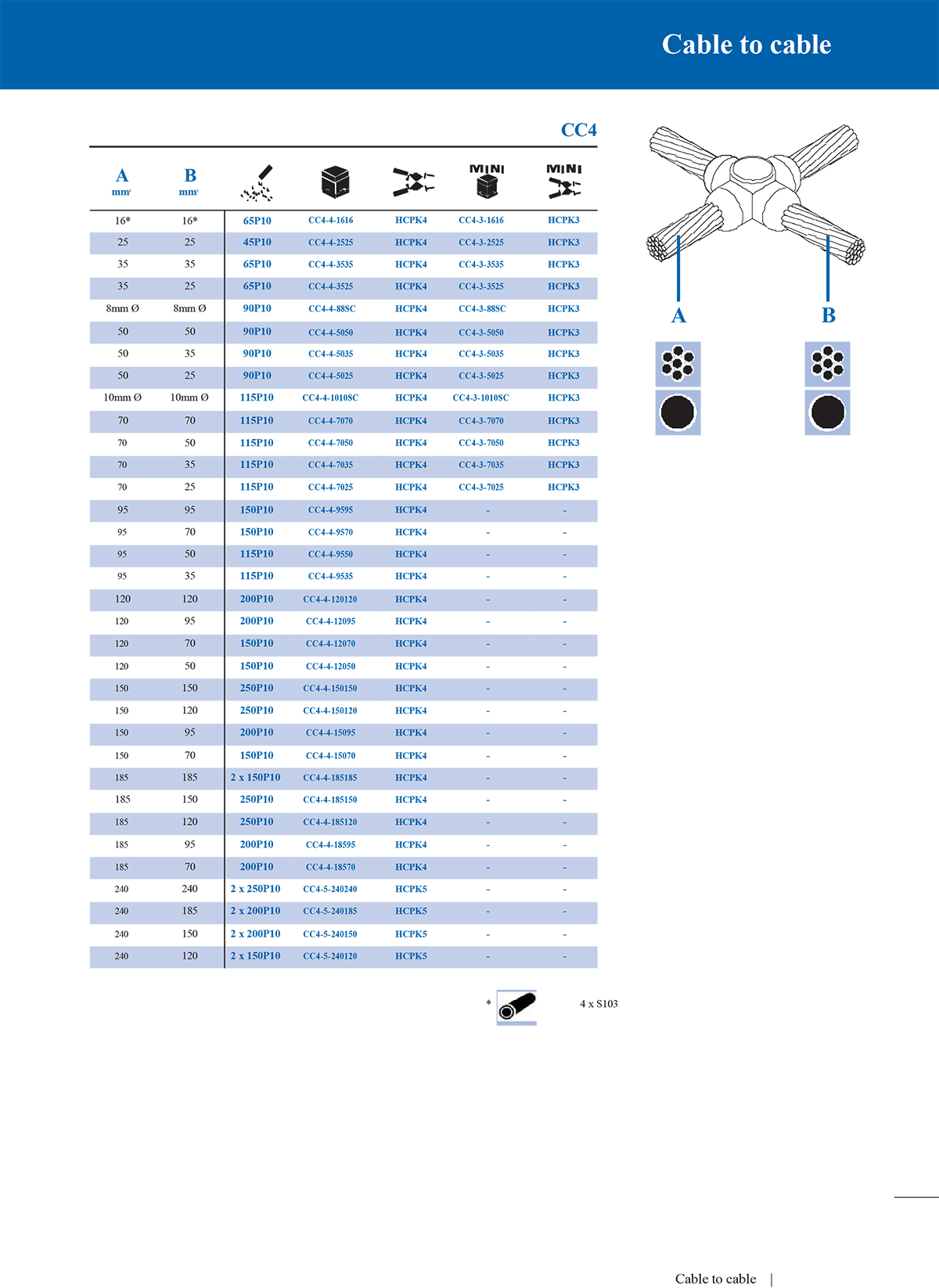
4. Cross connection mould
Cross moulds are used for cross-connection of two conductors. Usually, when building a grounding grid, such connections are required at the intersection of steel bars or bare copper wires.
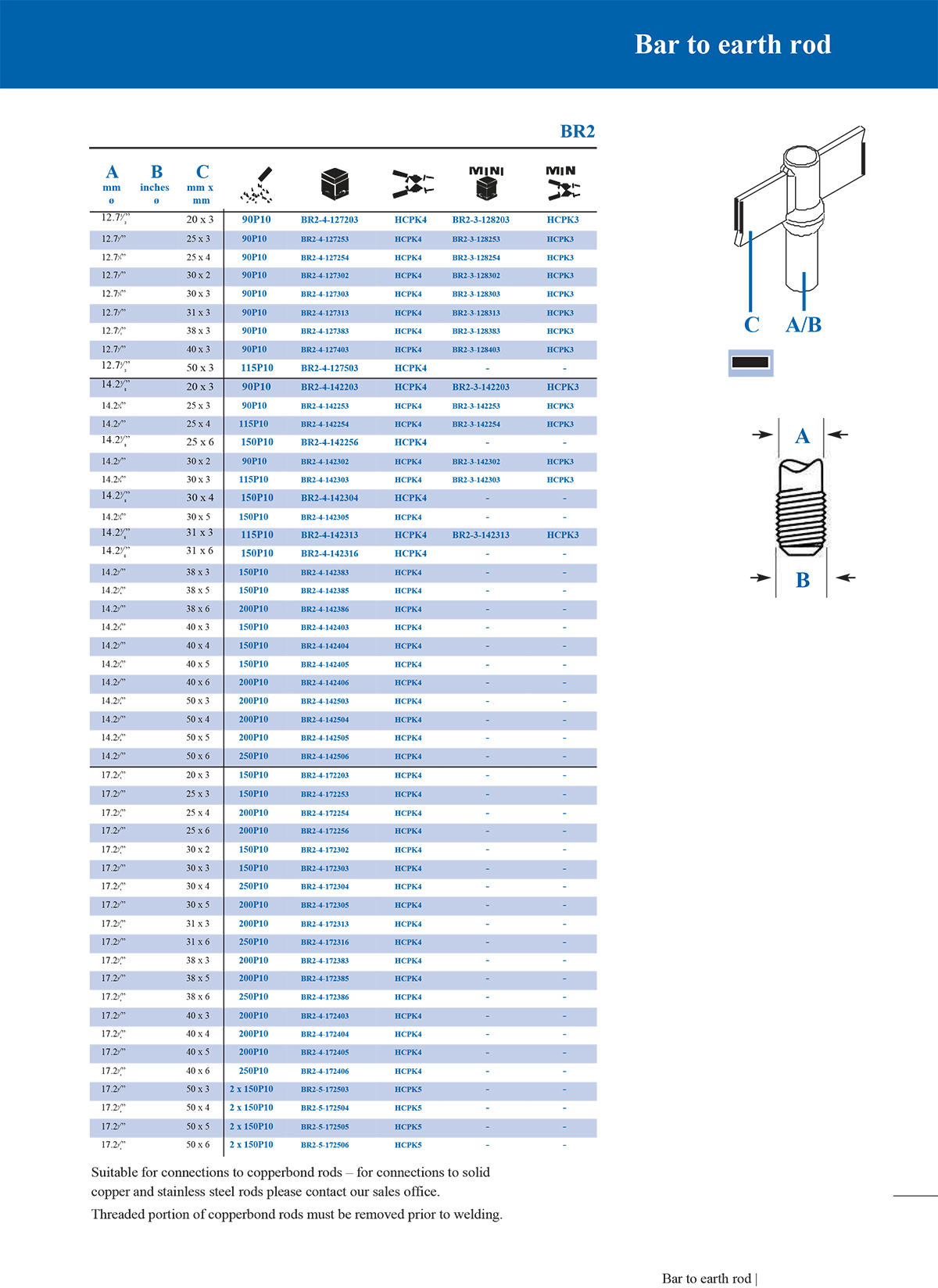
5. Termination connection mould
The termination mould is used for the fusion connection between the conductor and the terminal, ground rod or grounding electrode, which is suitable for building a reliable grounding grid terminal.
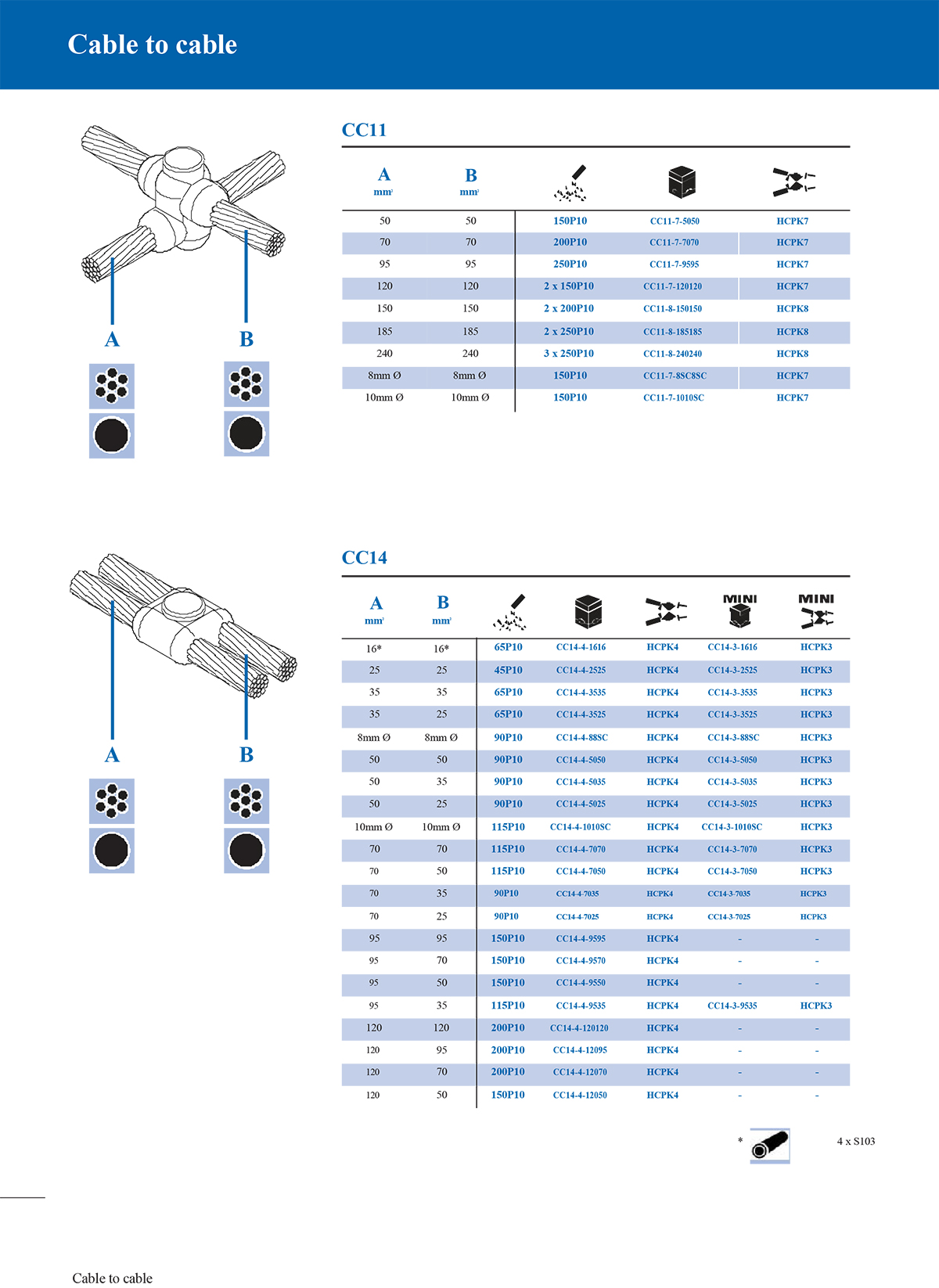
6. Stereoscopic connection mould
Stereoscopic moulds are used for welding in multi-direction, multi-angle, and multi-conductor intersections, such as the intersection of three or four cables, which requires a central welding point and has a more complex structure.
Selection principles for exothermic welding moulds
When selecting the type of mould, the following factors should be considered:
*Conductor type and specification size: Conductors of different sizes require moulds of matching sizes.
*Joint form: such as whether T-type, straight line or overlap form is required.
*Number of connected conductors: Two-way, three-way or multi-way connections require different cavity designs.
*Use environment: High-humidity, high-salt, and high-corrosion environments require higher-grade mould materials.
*Construction frequency: Frequent construction can select moulds with more repeated uses.
According to the actual needs of the construction site, non-standard moulds can also be customized to meet the welding requirements of complex connection structures.
Maintenance and service life management of moulds
Exothermic welding moulds are prone to wear or cracks under repeated high-temperature use. It is recommended to clean them after each use and store them properly in a dry and ventilated place. Regularly check whether there is residue, carbon deposit or crack in the mould cavity to avoid affecting the quality of the next welding.
The service life of the mould is usually between 50 and 100 times, depending on the mould material, operation method and use environment. Standard operation, preheating treatment, correct clamping and the use of appropriate welding powder ratio can help extend the mould life cycle.
Development trend of exothermic welding moulds
With the improvement of construction efficiency requirements and the improvement of automation, some exothermic welding moulds are gradually developing towards portable, modular and automatic ignition system compatibility. At the same time, the concept of green environmental protection promotes the popularization of low-smoke, low-residue exothermic powder matching moulds. For special industries, such as rail transit or offshore platforms, manufacturers are also developing mould products with higher corrosion resistance and higher thermal stability to adapt to more stringent application environments.
 English
English 简体中文
简体中文